Table of Contents
Color is a huge part of web design and design in general. Being able to use color properly goes a long way. Thankfully, CSS has a lot of color options that we can use. Let's go over all the ways we can use color in CSS.
 Aren't colors pretty?
Aren't colors pretty?
Red, Green, Blue
The rgb format, shorthand for red, green, and blue, is a popular way to specify colors. This format is probably the easiest to understand because all you have to do is specify what proportion of each color you want.
You can either go percentage-based, meaning 0% for none and 100% for all, or you can go byte-based, meaning 0 is for none and 255 is for all.
For example, if you wanted full-blown blue as your page's background color, you would set red and green to 0, but leave the last value at max, like so:
- CSS
Or if you wanted purple, you could specify half red and half blue, like so:
- CSS
Hexadecimal Value
You can use a color's hex value. To declare a hex value, you first start with a hash symbol, followed by six digits in base-16.
In base-16, the lowest digit is 0 and the highest is F, where each color is given two digits each. With hex values, if you wanted full-blown green, it would look like this:
- CSS
Hue, Saturation, Lightness Value
Another way to declare a color is to specify its hue, saturation and lightness. If you've ever used a color wheel:
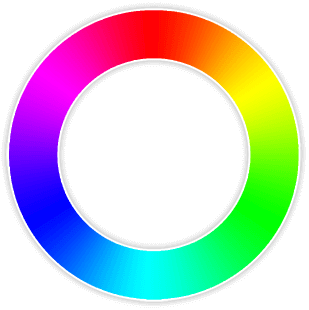 A color wheel with colors for days.
A color wheel with colors for days.
You can think of the hue as the degree, 0 to 360, on that wheel. On the wheel, 0 degrees is red, 120 degrees is green and 240 degrees is blue.
The saturation is a percentage describing how much color there should be. 0% would be a shade of gray whereas 100% is the full color.
The lightness is another percentage describing how light or dark the color should be, with 0% being black and 100% being white.
Here is an example of light green, using hsl:
- CSS
Alpha Transparency
CSS allows you to define colors that have an alpha, which basically means how transparent the color will be. This is a percentage, 0% is completely transparent and 100% is completely opaque, with the default being 100%. For example, if you wanted a semi-transparent green, you would set the alpha to 50%:
Red, Green, Blue, Alpha Value
You can define an alpha with the rgba format, which is shorthand for red, green, blue and alpha. Instead of three numbers defining how much red, green and blue is in the color, you now can use a fourth number to define the alpha, like so:
- CSS
The alpha is a value between 0 (entirely opaque) and 1 (entirely transparent), so 0.5 is equivalent to 50%.
Hue, Saturation, Lightness, Alpha Value
You can also define an alpha with the hsla format, which is shorthand for hue, saturation and lightness and alpha. Instead of three numbers defining how much hue, saturation and lightness is in the color, you now can use a fourth number to define the alpha. Below is an example usage:
- CSS
How cool is that? In our next lesson, we discuss how to work with fonts and text.
Resources
 Getting Started with TypeScript
Getting Started with TypeScript Getting Started with Express
Getting Started with Express Create an RSS Reader in Node
Create an RSS Reader in Node Git Tutorial: Learn how to use Version Control
Git Tutorial: Learn how to use Version Control How to Set Up Cron Jobs in Linux
How to Set Up Cron Jobs in Linux How to deploy a .NET app using Docker
How to deploy a .NET app using Docker How to build a Discord bot using TypeScript
How to build a Discord bot using TypeScript How to deploy a PHP app using Docker
How to deploy a PHP app using Docker How to deploy a Deno app using Docker
How to deploy a Deno app using Docker Getting Started with Sass
Getting Started with Sass How to Scrape the Web using Node.js and Puppeteer
How to Scrape the Web using Node.js and Puppeteer Using Push.js to Display Web Browser Notifications
Using Push.js to Display Web Browser Notifications
